Description
This blog explores an automated and scalable method for optimizing AWS Lambda memory configurations to enhance cost efficiency and performance. By leveraging AWS Compute Optimizer, memory recommendations are dynamically stored in AWS SSM Parameter Store, allowing for seamless integration with Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) deployments. An EventBridge Scheduler triggers a Lambda function periodically, fetching Compute Optimizer insights, analyzing them, and updating the corresponding SSM parameters. Additionally, an EventBridge rule listens for SSM Parameter Store updates and triggers a Lambda function to adjust the memory configuration dynamically, ensuring continuous optimization of Lambda function memory allocations with minimal manual intervention.
Introduction
AWS Lambda offers a flexible way to run serverless applications, but selecting the optimal memory configuration can be challenging. Over-provisioning leads to unnecessary costs, while under-provisioning can impact performance. AWS Compute Optimizer provides recommendations for memory adjustments based on real-time usage data. Automating this process ensures continuous cost savings and optimal performance. Source code for this blog is available at https://github.com/zechariahks/aws-cost-optimizer-solution/tree/main/lambda
Architecture Overview
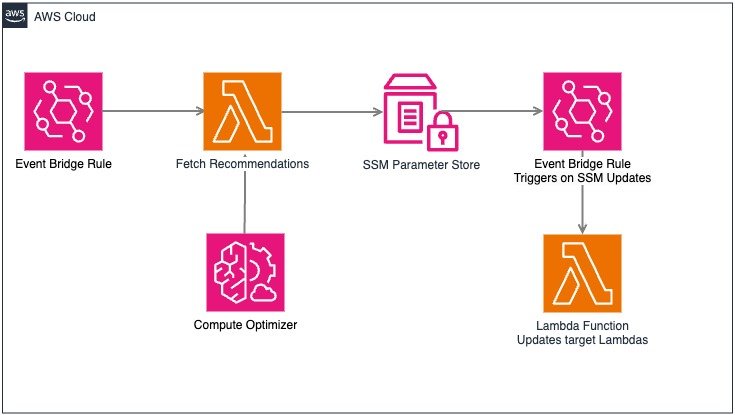
Components Used:
- AWS Compute Optimizer – Provides memory recommendations for Lambda functions.
- AWS SSM Parameter Store – Stores optimal memory configurations.
- AWS Lambda (for automation) – Fetches recommendations and updates parameters.
- Amazon EventBridge Scheduler – Triggers the optimization workflow periodically.
- Amazon EventBridge Rule – Listens for SSM parameter updates and triggers Lambda updates.
- AWS CloudFormation/Terraform – Dynamically references SSM parameters during deployment.
Implementation Steps
Step 1: Enable AWS Compute Optimizer for Lambda
Using AWS Console:
- Navigate to the AWS Compute Optimizer console.
- Click on Get Started and choose Opt In.
- Ensure Compute Optimizer has sufficient time (at least 24 hours) to analyze Lambda metrics.
Using AWS CLI:
Run below command on the terminal to enable Compute Optimizer.
aws compute-optimizer update-enrollment-status --status Active
Step 2: Store Memory Configurations in AWS SSM Parameter Store
Using AWS Console:
- Open the AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store.
- Click Create parameter and specify a name (e.g.,
/lambda/memory/MyFunction). - Set the parameter type as String and enter an initial memory value.
Using AWS CLI:
aws ssm put-parameter --name "/lambda/memory/MyFunction" --value "512" --type "String" --overwrite
Step 2: Create IAM Roles
Using AWS Console:
- Navigate to IAM Console
- Create role for Compute Optimizer Lambda:
- Choose Lambda as the service
- Add these policies:
- AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole
- Custom policy for Compute Optimizer access
- Custom policy for SSM Parameter Store access
- Create role for Update Lambda:
- Choose Lambda as the service
- Add these policies:
- AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole
- Custom policy for Lambda actions
- Custom policy for SSM Parameter Store access
Using AWS CLI:
Run below commands to create the required IAM Roles and policies.
# Create Compute Optimizer Lambda Role
OPTIMIZER_ROLE_ARN=$(aws iam create-role \
--role-name lambda_optimizer_role \
--assume-role-policy-document '{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "lambda.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}]
}' \
--query 'Role.Arn' \
--output text)
# Attach necessary policies
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--role-name lambda_optimizer_role \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole
aws iam put-role-policy \
--role-name lambda_optimizer_role \
--policy-name ComputeOptimizerAccess \
--policy-document '{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"compute-optimizer:GetLambdaFunctionRecommendations",
"lambda:ListFunctions",
"lambda:ListProvisionedConcurrencyConfigs",
"ssm:PutParameter"
],
"Resource": "*"
}]
}'
# Create Update Lambda Role
UPDATE_ROLE_ARN=$(aws iam create-role \
--role-name lambda_update_role \
--assume-role-policy-document '{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "lambda.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}]
}' \
--query 'Role.Arn' \
--output text)
# Attach necessary policies
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--role-name lambda_update_role \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole
aws iam put-role-policy \
--role-name lambda_update_role \
--policy-name UpdateLambdaConfig \
--policy-document '{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"lambda:UpdateFunctionConfiguration",
"ssm:GetParameter"
],
"Resource": "*"
}]
}'
Step 3: Create a Lambda Function to Fetch Compute Optimizer Recommendations
Now, we will create the lambda function that fetches the recommendations from Compute Optimizer.
Create a Python Lambda function (compute_optimizer_lambda.py):
On your local directory, create a file named compute_optimizer_lambda.py and add below code into it and save the file.
import boto3
def get_lambda_recommendations():
client = boto3.client('compute-optimizer')
response = client.get_lambda_function_recommendations()
ssm_client = boto3.client('ssm')
for recommendation in response['lambdaFunctionRecommendations']:
function_arn = recommendation['functionArn']
memory_size = recommendation['memorySizeRecommendationOptions'][0]['memorySize']
param_name = f"/lambda/memory/{function_arn.split(':')[-2]}"
print(f"Updating {param_name} to {memory_size}")
ssm_client.put_parameter(
Name=param_name,
Value=str(memory_size),
Type='String',
Overwrite=True
)
return {'status': 'Success'}
Deploy the Lambda function using AWS CLI:
You can deploy the lambda function using the Lambda console or run below commands to deploy it through CLI.
zip compute_optimizer_lambda.zip compute_optimizer_lambda.py
OPTIMIZER_FUNCTION_ARN=$(aws lambda create-function \
--function-name compute_optimizer_lambda \
--runtime python3.13 \
--role "$OPTIMIZER_ROLE_ARN" \
--handler compute_optimizer_lambda.handler \
--zip-file fileb://compute_optimizer_lambda.zip \
--timeout 120 \
--query 'FunctionArn' \
--output text)
Step 4: Schedule Execution with EventBridge
Using AWS Console:
- Open Amazon EventBridge Console.
- Choose Rules on the left side.
- Create a new rule with a schedule to trigger the
compute_optimizer_lambdaLambda function periodically (e.g., daily or weekly).
Using AWS CLI:
On the terminal, run below commands to create the Event Bridge rule that runs daily once. Adjust the schedule as per your need.
aws events put-rule --schedule-expression "rate(1 day)" --name LambdaMemoryOptimization
aws events put-targets --rule LambdaMemoryOptimization --targets "Id"="ComputeOptimizerLambda","Arn"="$OPTIMIZER_FUNCTION_ARN"
aws lambda add-permission \
--function-name "compute_optimizer_lambda" \
--statement-id "EventBridgeInvoke" \
--action "lambda:InvokeFunction" \
--principal events.amazonaws.com
Step 5: Create an EventBridge Rule to Detect SSM Parameter Updates and Adjust Lambda Configuration
Follow below steps to create the Lambda function that updates the target lambdas that need modifications recommended by Compute Optimizer. This lambda pulls the saved configurations from SSM Parameter store.
Create a Lambda function to update memory configuration (update_lambda_memory.py):
On your local directory, create a file named update_lambda_memory.py and add below code into it and save the file.
import boto3
def update_lambda_memory(function_name, memory_size):
lambda_client = boto3.client('lambda')
lambda_client.update_function_configuration(
FunctionName=function_name,
MemorySize=int(memory_size)
)
def lambda_handler(event, context):
ssm_client = boto3.client('ssm')
function_name = event['detail']['name'].split("/")[-1]
response = ssm_client.get_parameter(Name=event['detail']['name'])
memory_size = response['Parameter']['Value']
print(f"Updating {function_name} to {memory_size}")
update_lambda_memory(function_name, memory_size)
return {'status': 'Updated Lambda memory'}
Deploy the Lambda function update_lambda_memory using AWS CLI:
You can deploy the lambda function using the Lambda console or run below commands to deploy it through CLI.
zip update_lambda_memory_function.zip update_lambda_memory.py
UPDATE_FUNCTION_ARN=$(aws lambda create-function \
--function-name update_lambda_memory \
--runtime python3.13 \
--role "$UPDATE_ROLE_ARN" \
--handler update_lambda_memory.handler \
--zip-file fileb://update_lambda_memory_function.zip \
--timeout 120 \
--query 'FunctionArn' \
--output text)
Configure EventBridge rule to trigger update_lambda_memory function:
Using AWS Console:
- Open Amazon EventBridge Console.
- Choose Rules on the left side.
- Create a new rule with to trigger the
update_lambda_memoryLambda function when SSM Parameters are updated. Check below CLI step for the specific event details to use.
Using AWS CLI:
On the terminal, run below commands to create the Event Bridge rule that invokes the lambda function when the SSM parameters are updated.
aws events put-rule --name "SSMParameterChangeRule" --event-pattern '{
"source": ["aws.ssm"],
"detail-type": ["Parameter Store Change"],
"detail": { "operation": ["Update"], "name": [{"prefix": "/lambda/memory/"}] }
}'
aws events put-targets --rule SSMParameterChangeRule --targets "Id"="UpdateLambdaMemory","Arn"="$UPDATE_FUNCTION_ARN"
aws lambda add-permission \
--function-name "update_lambda_memory" \
--statement-id "EventBridgeInvoke2" \
--action "lambda:InvokeFunction" \
--principal events.amazonaws.com
Step 6: Create/Modify IaC (CloudFormation Template) to Use SSM Parameters
This is an example CloudFormation template that is used to deploy a sample Lambda function with an initial memory configuration.
Example in CloudFormation:
Create a file named sample-lambda.yml on your local directory and add below code to it.
Resources:
LambdaExecutionRole:
Type: 'AWS::IAM::Role'
Properties:
RoleName: basic-lambda-execution-role
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- lambda.amazonaws.com
Action:
- 'sts:AssumeRole'
ManagedPolicyArns:
- 'arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole'
Path: '/'
MyLambdaFunction:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Function
Properties:
FunctionName: MyFunction
MemorySize: !Ref MemoryParameter
Handler: index.lambda_handler
Role: !GetAtt LambdaExecutionRole.Arn
Code:
ZipFile: |
def lambda_handler(event, context):
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': 'Hello from Lambda!'
}
Runtime: python3.12
Parameters:
MemoryParameter:
Type: AWS::SSM::Parameter::Value<String>
Default: /lambda/memory/MyFunction
Deploy the CloudFormation Stack using CLI
On your terminal, run below command to create the sample CloudFormation stack. Once the stack is deployed, it will take approximately 24 hours for Compute Optimizer generate recommendations for the lambda that was deployed as part of this template.
aws cloudformation create-stack --stack-name lambdastack --template-body file://sample-lambda.yml --capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAMDeploy the infrastructure stack
If you want to use CloudFormation to create all the resources described above, you can clone the repository https://github.com/zechariahks/aws-cost-optimizer-solution and deploy the lambda optimizer template.
aws cloudformation create-stack --stack-name lambda-cost-optimization --template-body file://lambda-optimizer-template.yml \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM
Script to invoke lambda function to generate recommendations
As per the documentation, lambda function must be invoked at least 50 times in the lat 14 days to generate recommendations. You can use below script for invoking your lambda function.
#!/bin/bash
FUNCTION_NAME="MyFunction"
for i in {1..100}; do
aws lambda invoke \
--function-name $FUNCTION_NAME \
--invocation-type Event \
--cli-binary-format raw-in-base64-out \
--payload '{"message": "test"}' \
/dev/null > /dev/null 2>&1
echo "Invocation $i sent"
# Optional: Add small delay to prevent throttling
sleep 0.1
done
echo "All invocations completed"
After the solution is deployed in the account, wait for 24 hours and you will see lambda recommendations as below. The event bridge rules will get triggered as per the schedule and update the memory configurations for the relevant Lambda functions.
Conclusion
This solution ensures continuous Lambda memory optimization using AWS Compute Optimizer, SSM Parameter Store, and EventBridge. This approach eliminates the need for manual updates and automates the entire workflow for updating the Lambda functions dynamically based on Compute Optimizer recommendations.
Resources:
Github Repository: https://github.com/zechariahks/aws-cost-optimizer-solution
AWS Compute Optimizer documentation: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/compute-optimizer/latest/ug/getting-started.html
AWS Lambda documentation: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/welcome.html
Clean up
If you used CLI commands to create the resources, then run the following commands to clean up the resources. Update the commands appropriately to align with your resource names.
# 1. Delete EventBridge Rules
aws events remove-targets --rule LambdaMemoryOptimization --ids "ComputeOptimizerLambda"
aws events delete-rule --name LambdaMemoryOptimization
aws events remove-targets --rule SSMParameterChangeRule --ids "UpdateLambdaMemory"
aws events delete-rule --name SSMParameterChangeRule
# 2. Delete Lambda Functions
aws lambda delete-function --function-name compute_optimizer_lambda
aws lambda delete-function --function-name update_lambda_memory
# 3. Delete IAM Roles and their policies
aws iam delete-role-policy --role-name lambda_optimizer_role --policy-name ComputeOptimizerAccess
aws iam detach-role-policy --role-name lambda_optimizer_role --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole
aws iam delete-role --role-name lambda_optimizer_role
aws iam delete-role-policy --role-name lambda_update_role --policy-name UpdateLambdaConfig
aws iam detach-role-policy --role-name lambda_update_role --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole
aws iam delete-role --role-name lambda_update_role
# 4. Clean up any SSM Parameters created
aws ssm get-parameters-by-path --path "/lambda/memory/" --recursive | \
jq -r '.Parameters[].Name' | \
while read param; do
aws ssm delete-parameter --name "$param"
done
# 5. Disable Compute Optimizer (optional - only if you don't need it for other resources)
aws compute-optimizer update-enrollment-status --status Inactive
If you used CloudFormation template to create the infrastructure, then run below command to delete the stack.
aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name lambda-cost-optimizationFeedback
Any feedback/suggestions/issues are welcome through Github repository https://github.com/zechariahks/aws-cost-optimizer-solution/issues
